A Brief History of Artificial Intelligence in Video Games, From “Pac-Man” to “Dragon’s Dogma 2”

Ask video game characters out loud and watch them respond to you improvised thanks to generative artificial intelligence (AI). This is promised by Ubisoft’s Neo NPC or Nvidia ACE, prototypes presented respectively at the Game Developers Conference in San Francisco on March 20 and at the Consumer Electronics Show in Las Vegas in January.
For the moment, no game on the market integrates these techniques using neural learning, which consumes resources and energy. But they raise the question: Will they supersede the traditional AI that, in video games, defines the way the world works and the behavior of non-player characters (NPCs)?
Since its birth, AI has established a relationship with gaming. We find traces of this as early as 1956, when the names and principles of this scientific discipline were formulated during a workshop at Dartmouth College, University of New Hampshire. “Among the aims, was to create a chess player”Explains Eric Jacopin, programmer at Hawkeswell Studio and former head of the computer laboratory at the Special Military School in Saint-Cyr.
Ghosts and earthworms
However, we had to wait for the first success of the arcade game for the general public to discover playful AI. popularity of Pac-Man (1980) wouldn’t have been the same without AI animating the four ghosts confronting the ravenous hero. It’s thanks to her that they alternate between different roles – neutral, aggressive or evasive – in the popular Namco title.
Guided by a mathematical model of an automaton with a finite number of states, they move from one to the next based on the player’s actions and the duration assigned to each behavior. Each ghost’s individual personality is superimposed on this system. For example, red is a tireless hunter while pink is an ambush.
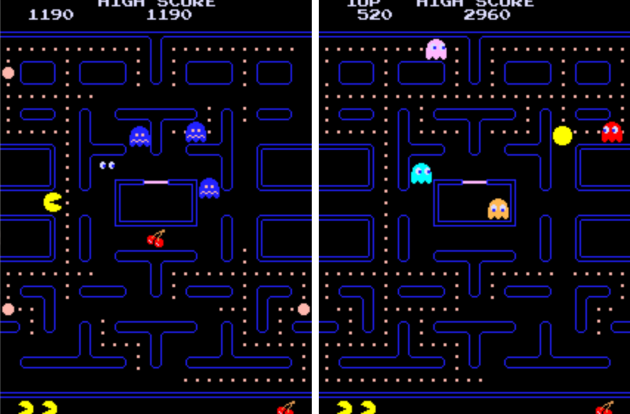

Revolutionary in the early days of video games, these AIs no longer baffle experienced players. “We can avoid behaviors because what is being modeled is so simpleEric Jacopin says. Ghosts are a bit like earthworms, with only three hundred neurons in their brains and only reacting to simple stimuli. » In 1982, a book was published on learning how to anticipate them: How to win at Pac-Man (Pocket Books, Untranslated).
Mrs. Pac-Man (1982), designed by Americans at General Computer Corporation, then complicates the situation. The machine integrates an element of chance into the routines of state changes and adversaries. “Humans are very good at anticipating things they’ve seen before. So when the ghosts became more random, the difficulty increased and so did the fun. In the context of AI, this translates as moving from a deterministic problem to a non-deterministic problem.Summarizes Tommy Thompson, an AI consultant for the video game industry who popularizes these topics on the AI and Games YouTube channel.
You have 61.55% of this article left to read. The rest is reserved for subscribers.





